What’s Causing Your Leg Pain?
Leg pain can be a distressing symptom with a wide range of potential causes, from minor injuries to serious medical conditions. Understanding the root cause is crucial for effective treatment and management. Here are ten common causes of leg pain, detailed to help you identify and address your symptoms.
Common Leg Pain Symptoms
Leg pain can manifest in several ways, depending on the cause. Here are some of the most common symptoms:
- Aching or Throbbing Pain: Often felt deep within the leg, this type of pain can be constant or intermittent, worsening with activity or prolonged standing.
- Sharp, Shooting Pain: This sudden and intense pain may radiate down the leg and is often associated with nerve-related issues, such as sciatica.
- Muscle Cramps: Sudden, tight, and intense muscle contractions, commonly occurring in the calf, are often referred to as “charley horses.”
- Swelling and Redness: Inflammation or swelling of the leg, accompanied by redness, can indicate an infection, blood clot, or other serious conditions.
- Numbness or Tingling: A sensation of pins and needles or loss of feeling in the leg may point to nerve compression or damage.
- Weakness: A feeling of weakness or heaviness in the leg can interfere with mobility and may suggest an underlying neurological or muscular disorder.
Possible Causes of Leg Pain
The causes of leg pain are diverse and can range from minor injuries to serious medical conditions. Some common causes include:
- Muscle Strains and Sprains: Overuse, sudden movements, or injuries can lead to muscle and ligament damage.
- Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD): Reduced blood flow due to narrowed arteries can cause pain, especially during physical activity.
- Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): A blood clot in a deep vein, usually in the leg, can cause pain, swelling, and redness.
- Sciatica: Compression of the sciatic nerve can cause sharp pain that radiates from the lower back down the leg.
- Arthritis: Inflammation of the joints can lead to chronic leg pain, particularly in older adults.
- Infections: Cellulitis and other infections can cause localized pain, redness, and swelling.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While some leg pain can be managed with rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE), certain symptoms warrant prompt medical evaluation:
- Severe pain that does not improve with rest
- Signs of infection, such as fever or increasing redness
- Sudden swelling or pain, particularly if you have risk factors for DVT
- Loss of sensation or movement in the leg
- Pain following an injury or accident
1. Muscle Cramps and Strains Leg Pain
Muscle Cramps: These are abrupt, involuntary contractions of muscles that can cause intense pain. They often occur due to dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, overexertion, or prolonged periods of inactivity.
Prevention includes staying hydrated, maintaining electrolyte balance, and warming up before physical activities.
Muscle Strains: These injuries occur when muscles or tendons are overstretched or torn, typically due to heavy lifting, sudden movements, or overuse during sports and other physical activities. Symptoms include localized pain, swelling, and difficulty moving the affected muscle. Treatment generally involves rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE), along with gradual stretching and strengthening exercises as healing progresses.
2. Ligament Injuries
Ligament injuries, such as sprains, involve the stretching or tearing of ligaments, which connect bones at joints. Common areas for sprains include the ankles and knees, often resulting from twisting or impact injuries. Symptoms include swelling, bruising, and joint instability.
3. Bone Fractures
Bone fractures range from hairline cracks to complete breaks and can occur due to trauma from accidents or falls, or repetitive stress in activities like running. Symptoms include severe pain, swelling, and difficulty bearing weight. Treatment varies from immobilization with casts or splints to surgical intervention to realign and stabilize the bone.
4. Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) is caused by narrowed arteries that reduce blood flow to the limbs, usually due to atherosclerosis. Symptoms include claudication (pain during walking), numbness, and slow-healing sores. Risk factors include smoking, diabetes, and high cholesterol. Management involves lifestyle changes, medications to improve blood flow, and in severe cases, surgical procedures to restore circulation.
5. Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) involves the formation of blood clots in deep veins, typically in the legs. Symptoms include swelling, pain, warmth, and redness in the affected area. Risk factors include prolonged immobility, surgery, and certain medical conditions. DVT requires immediate medical attention to prevent complications such as pulmonary embolism. Treatment includes anticoagulant medications and compression therapy.
6. Nerve Compression
Conditions like sciatica result from compression or irritation of the sciatic nerve, which runs from the lower back down the legs. Causes include herniated discs and spinal stenosis. Symptoms include sharp, shooting pain, tingling, or numbness radiating from the lower back to the foot. Treatment options include physical therapy, medications, and sometimes surgery to relieve nerve pressure.
7. Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy involves damage to peripheral nerves, leading to pain, burning, tingling, or numbness, particularly in the legs and feet. Common causes include diabetes, infections, and exposure to toxins. Managing the underlying condition, along with medications and lifestyle modifications, can help alleviate symptoms and improve nerve function.
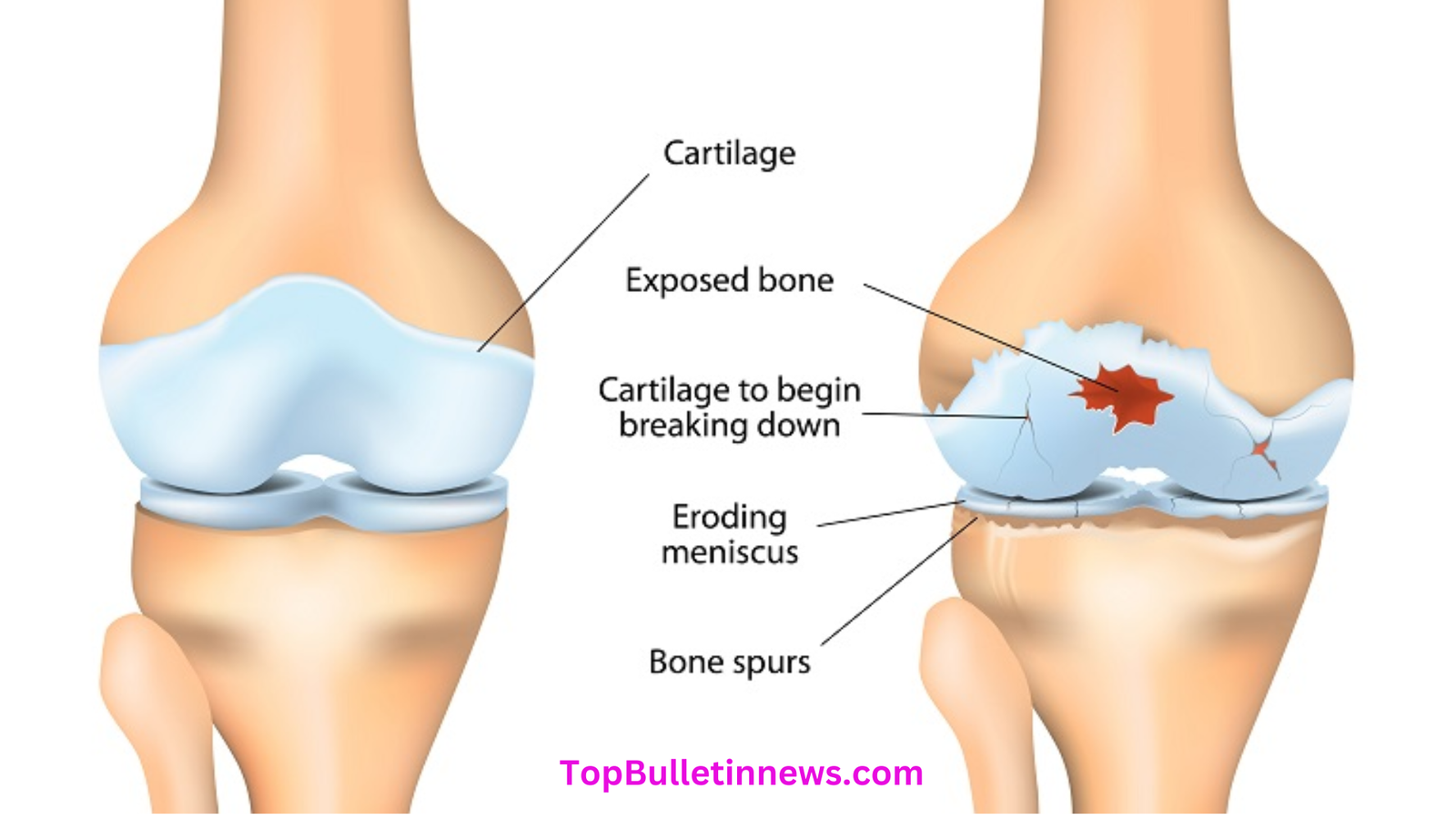
8. Joint Disorders
Joint disorders such as arthritis cause inflammation and pain in the joints. Osteoarthritis results from the degeneration of cartilage, while rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder. Symptoms include pain, stiffness, and swelling, often worsening with activity. Treatment includes medications to reduce inflammation, physical therapy, and in severe cases, joint replacement surgery.
9. Infections
Infections like cellulitis and osteomyelitis can cause leg pain. Cellulitis is a bacterial infection of the skin and tissues beneath, leading to redness, swelling, and tenderness. Osteomyelitis is an infection in the bone, often causing severe pain, fever, and swelling. Both conditions require prompt medical attention and treatment with antibiotics, and sometimes surgical intervention for osteomyelitis.
10 Important Health benefits of the common sunflower
Conclusion:
Leg pain can arise from a variety of causes, each requiring specific treatments and management strategies. Whether your pain stems from muscle cramps, injuries, circulatory issues, or more complex conditions like nerve damage or infections, understanding the underlying cause is crucial for effective relief. If you experience persistent, severe, or worsening leg pain, it’s important to seek medical evaluation to determine the appropriate course of action. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications and help maintain your mobility and quality of life.